Introduction
Cancers generally known as head and neck cancers typically begin in squamous cells lining the moist, mucosal surfaces in the head and neck. The squamous cell cancers are also called assquamous cell carcinomas. These cancers can also start in the salivary glands but this is a lot less common. The salivary glands have many different kinds of cells that can all develop into cancer thus there are many types of this cancer.
Signs and Symptoms
The most common symptoms of head and neck cancers can include a sore or lump that persists, a sore throat for prolonged periods, difficulty/pain swallowing and a change in the voice. Take note that these symptoms can also be caused by less serious conditions so do not panic if you have any of them. If you have any of these symptoms, consult your physician. There are also symptoms that affect certain areas of the head and neck depending on where the cancer develops.
Causes and Risk Factors
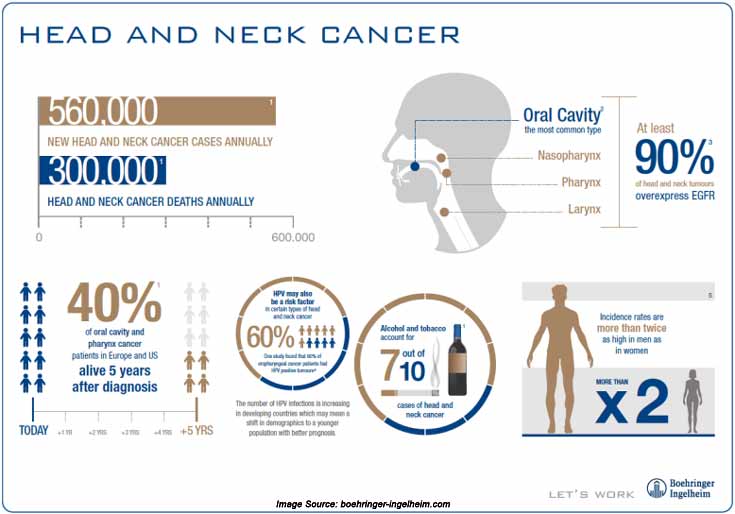
The two top risk factors for head and neck cancers are alcohol and tobacco use. About 75% of head and neck cancers are related to these risk factors. Those who use tobacco products and consume alcohol regularly are at higher risk compared to those who use either tobacco or alcohol only. However, these are not risk factors for salivary gland cancers.
Infections with certain types of human papillomavirus (HPV) that can cause cancer is also a risk factor for certain head and neck cancers. In the US, there is an increasing* incidence of oropharyngeal cancers from HPV infection while those from other causes are declining. The other risk factors are as follows:
Types
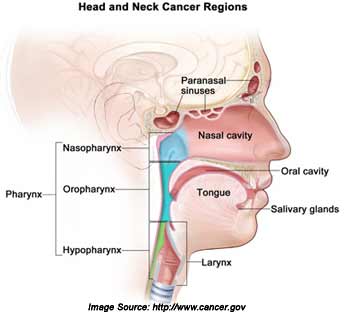
The types of head and neck cancers depend on where the cancer develops. It can be in the oral cavity, pharynx, larynx, paranasal sinuses and nasal cavity or salivary glands.
Tests and Diagnosis
Diagnosing head and neck cancers starts with evaluating the medical history of the patient and preforming physical examination. Then diagnostic tests can be ordered depending on the signs and symptoms of the patient. Examining a tissue sample under a microscope is completely necessary to confirm diagnosis of cancer. If cancer is diagnosed, the next step is to discover the stage of the disease and its extent. This may involve an examination in an operating room under anesthesia, x-rays and other imaging procedures and laboratory tests. Knowing the particular stage of the disease is crucial in making a treatment plan.
Treatments and Medications
Treatment for head and neck cancer may include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy or a combination of any of these treatments. The treatment plan depends on the particular case of the patient including several factors like location of the tumor, stage of the cancer, age of the patient and general health.
Precautions and Self Care
Regular follow-up care is crucial after treating head and neck cancer in order to make sure it has not returned or that a second primary cancer has not developed. Follow-up care may include exams of the stoma, regular dental exams, physical exams, blood tests, x-rays, computed tomography, positron emission tomography or magnetic resonance imaging scans. Thyroid and pituitary gland function may also be monitored especially if the cancer was treated using radiation. Patients who are smokers and heavy drinkers are asked to stop since these can reduce* effectiveness of treatment and increase* the chance that a second primary cancer will develop.





No comments:
Post a Comment